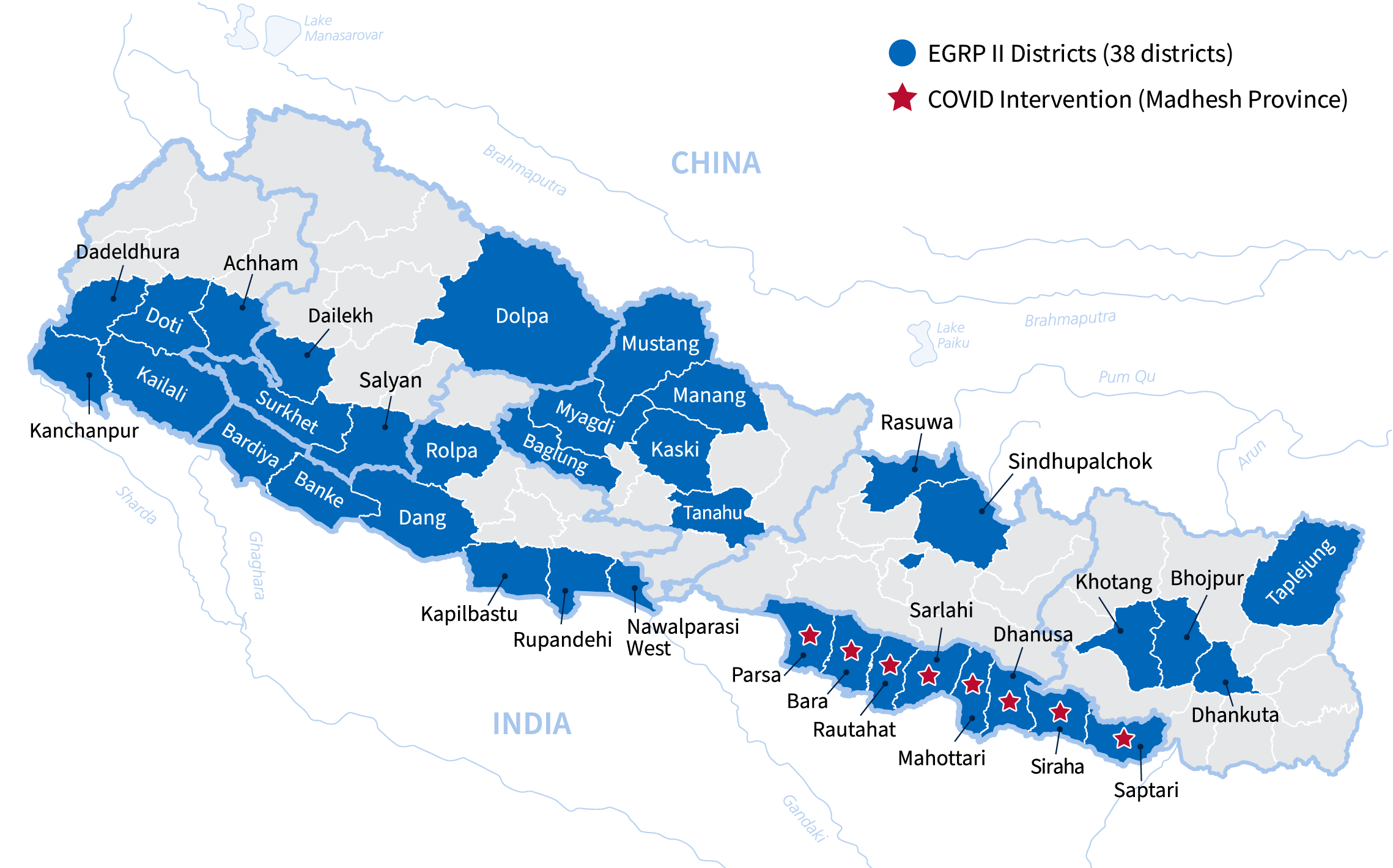
Building on the foundation of the first EGRP from 2015 to 2020, EGRP II (2020-2022) aimed to improve early grade literacy for students in grades 1-3 in Nepali public schools. EGRP II supported activities across all program districts, plus activities for a community- and home-based intervention response to COVID-19 in Madhesh province, which is described in more detail below.
EGRP II activities included:
- Supporting the development and rollout of the Government of Nepal’s “Integrated Curriculum” and continuing to scale up the government’s NEGRP.
- Building municipal- and provincial-level capacity for delivering early grade reading services.
- Improving local governments’ ability to provide effective teacher professional support.
- Supporting continuity of learning in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
These activities were conducted in 38 target districts across all 7 of Nepal’s provinces.
The CB-EGRA instrument was the key tool used in the evaluation. During the baseline evaluation, a small pilot study was conducted to link student scores on the CB-EGRA to their scores on typical EGRA subtasks.
The sample of students assessed for the overall intervention consisted of a mix of students who spoke Nepali as their mother tongue, and students who spoke other languages as their mother tongue.
COVID-19 Intervention in Madhesh Province
In addition to EGRP II implementation, a customized community- and home-based learning approach was targeted to 8 districts in Madhesh Province that were heavily impacted by COVID-19. These interventions included:
- teacher training on flexible learning approaches
- distribution of more than 2,000 tablets pre-loaded with offline learning content, and
- provision of books and stationery packs.
The impact of this intervention was evaluated separately from EGRP II. The sample of students assessed for the COVID-19 intervention consisted only of students who spoke other languages (not Nepali) as their mother tongue. View the impact of the program's catch-up learning activities on the Intervention Impact page.
More detailed information about EGRP II may be found in the Baseline Report: Program Impact on Student Reading Performance in the Early Grades (PDF, 6.6 MB).